What’s in this edition:
- News/Publications to follow
- Financial considerations for your restaurant business plan
- Industry metrics for guidelines
- Fast food preferences in the US
- Food delivery app preferences
Public Information to Follow
Financial Considerations for your Business Plan
Irregular cash flow
During tough economic times, people tend to cut back on eating out. Additionally, restaurants have to compete with new food places and other food retailers for a chunk of the market, and the number of customers they get can change depending on the day, time of day, and season (tourists or lack of).
Variable food costs
Prices for food can change quickly because of different factors like the weather and global demand. When this happens, restaurants can have a hard time keeping their margins and profits steady. To avoid losing money, they might have to adjust their menu prices, or change the items they serve or how much they serve. But, franchise restaurants may not have to worry as much about price changes because they have contracts with suppliers that cover a high volume of food.
Staffing
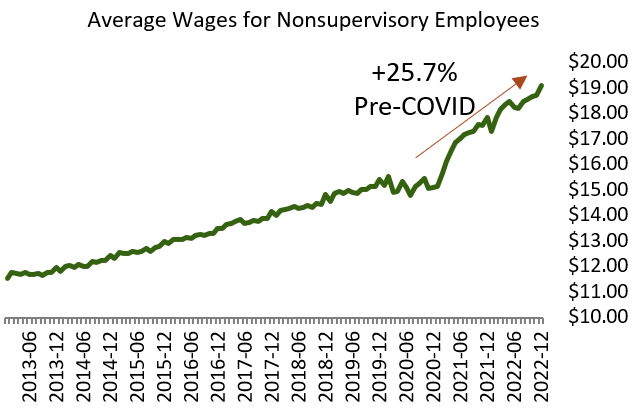
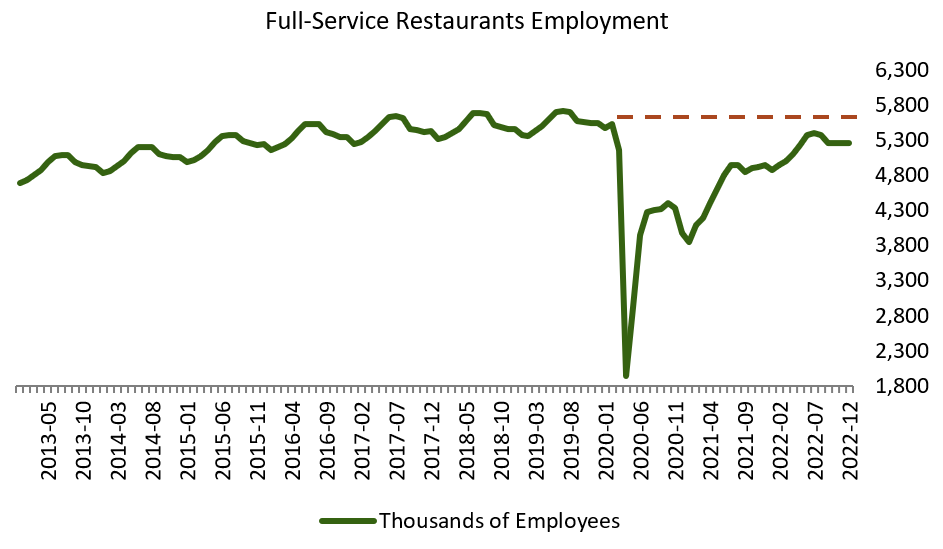
When a restaurant doesn’t have enough staff, it can really hurt their business by making it hard to serve customers and make money. Full-service restaurants can have trouble keeping their staff and finding new workers to cover shifts, especially since many people only want to work part-time. Additionally, since the pandemic, the cost of staffing has increased by 25.7%, which has further added to the challenges faced by full-service restaurants.
Profit drivers
- Maximizing Capacity – Full-service restaurants need to maintain high customer traffic to fill up their available tables, and they use loyalty programs, advertising, promotions, and efficient service to do this.
- Average Check Size – To generate more sales, restaurants can increase the average check size by adjusting menu prices, promoting daily specials, training wait staff to suggest upgrades, and offering high-margin alcoholic beverages.
- Managing Prime Cost – Managing prime cost (food and beverage costs plus labor costs) is crucial for profitability, and restaurants can improve this by effective purchasing, product handling, menu pricing, hiring practices, training, and staff scheduling.
Recent Industry Metrics (Companies <$5M revenue)
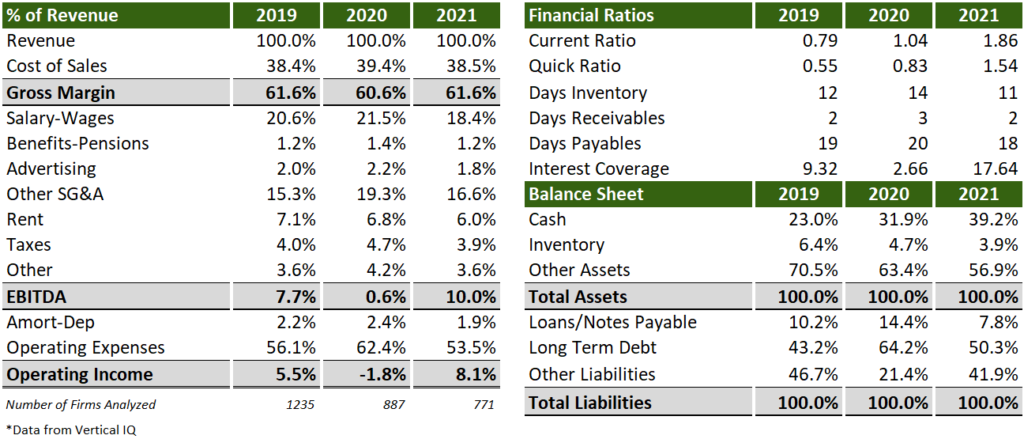
Highlights from this vertical analysis and financial ratios:
- Hoarding cash is driving up assets.
- Declining inventory likely driven by shortages or reducing the number of menu items. However, this slight decline (as related to pre-pandemic) may be an indication that restaurants are successfully reducing waste and optimizing operations.
- Increased EBITDA margins primarily driven by lower salaries-wage total costs from the lack of the industry to return to pre-pandemic levels.
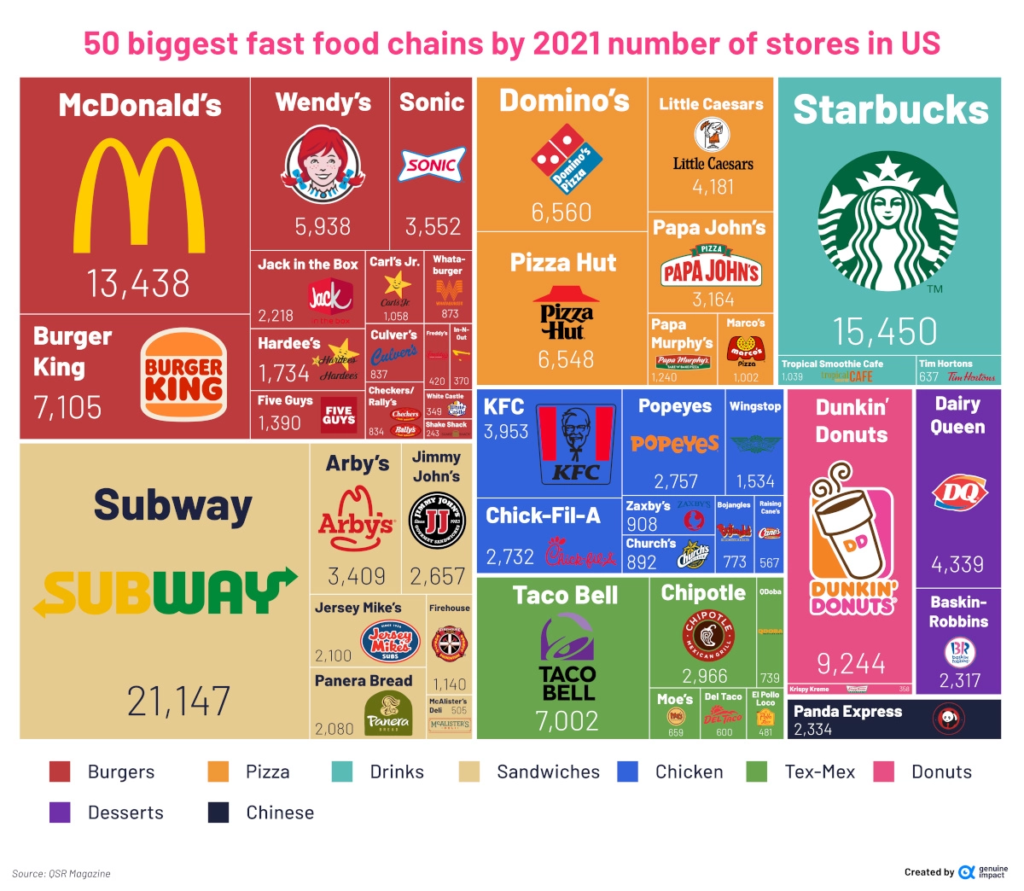
Fast Food in the United States
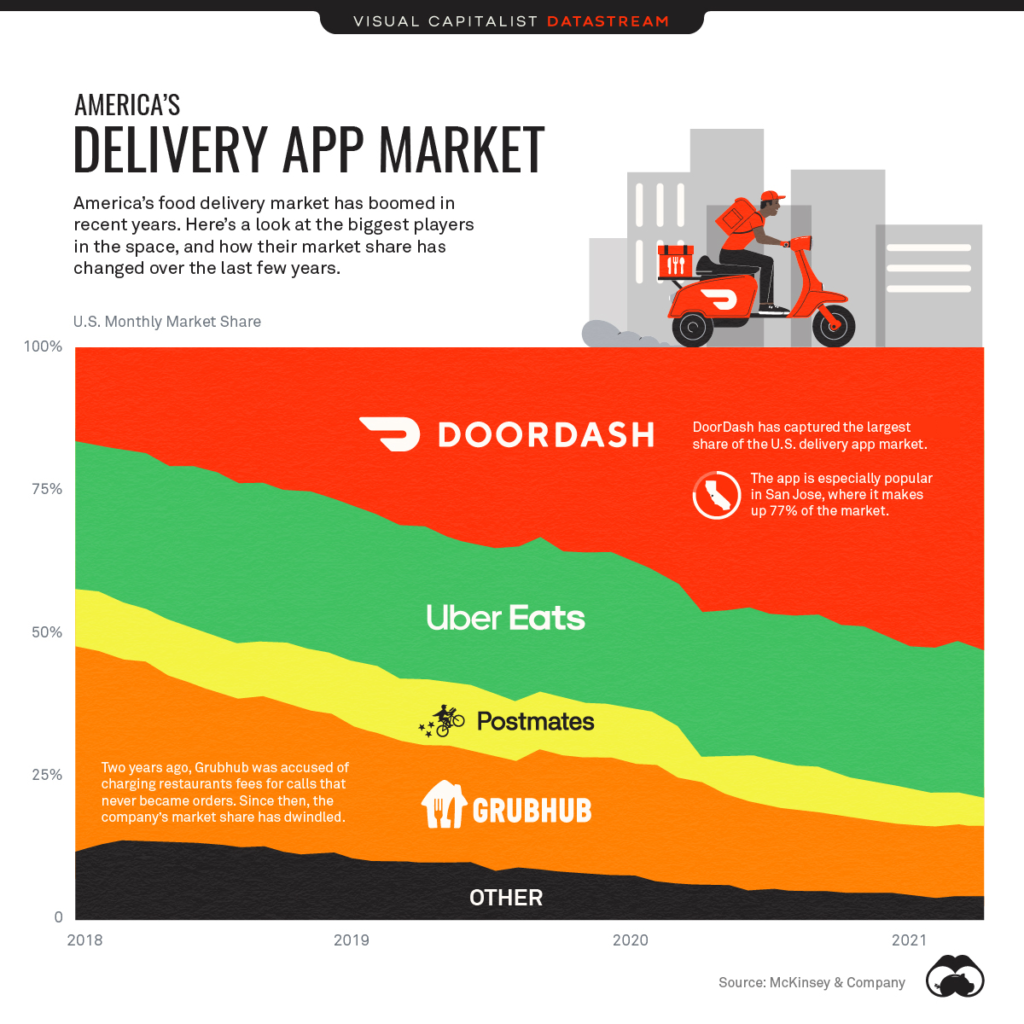
Food Delivery
For more information on building financial models see here.
Please contact me here if you found this useful or want more information.

